语法概述
英语当中所有的语法可以归纳位10+9+8,10个词性,9个句子成分,8个句型。这就是英语中所有相对应的语法。
动词
动词的分类
英语中的动词可以分为实义动词、助动词、前台动词和系动词。其中助动词与情态动词是不能够充当谓语的。
实义动词
实义动词也就是具有实际意义的动词。实义动词可以分为及物动词和不及物动词。
助动词
协助主要动词构成位于的单词。没有实际意义,构成时代、语态、否定句、强调句。主要又have/do/be.接下来我们举几个例子简要介绍:
be动词:
- He is always spilling things. (be 构成进行时)
- This sentence was written. (be 构成被动语态)
have: - I have read many books. (have 帮助完成完成时)
- I have be dreaming it for so long. (have 帮助完成进行时)
do: - He didn’t put his coffee in a cup with a lid.(帮助完成否定句)
- Why did you do that?(帮助完成疑问句)
- Do come with us.(帮助完成强调句)
情态动词
情态动词具有词义,但是需要与实意动词一起使用。情态动词主要有:
- may,might
- can,could,be able to
- will, would
- shall,should
系动词
系动词是指具有实际意义且其后能够直接增加表语的一类动词,其主要由:
- 状态系动词(be系列,am\is\are\was\were…)
- 感官动词系列(feel,look,smell,sound,taste,seem,appear…)
- 变化系动词(get,become,turn,grow…)
- 持续系动词 (keep,stay,remain,rest…)
动词的四大语法
时态
英语中一共有十六种时态,但是常用的只有六种。
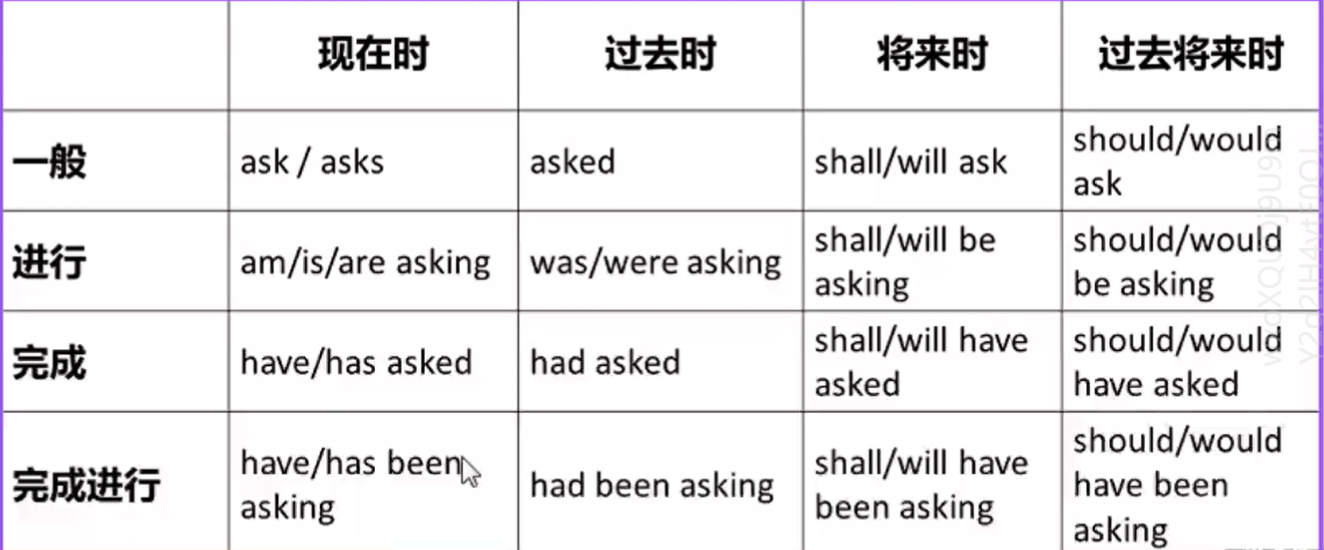
对于常用的6种,我们可以归纳为大时间、小时态。首先我们要分析全文中描述的时间:
- 过去:一般过去时、过去完成时、现在完成时
- 现在:一般现在时、现在进行时
- 将来:一般将来时
一般现在时
- 形式
- 肯定形式:第三人称但是用三单;其他使用原型
- 否定形式:主语+do/does+not+原型
- 疑问形式:疑问词+do/does+主语+谓语动词原型
- 用法:
- 现阶段发生的事情:I feel great!
- 经常性、习惯性发生的动作: I never drink coffee before 12.00 o’clock.
- 表示客观真理: Teachear told us that the earth is running around the sun.
一般过去时
- 形式
- 肯定形式:主语+动词过去式
- 否定形式:主语+did+not+原型
- 疑问形式:疑问词+did+主语+谓语动词原型
- 用法:
- 过去发生的事情:I went to the hospital to have a test yesterday.
一般将来时
- 形式
- 肯定形式:主语+will+动词过去式
- 否定形式:主语+won’t(will not)+原型
- 疑问形式:疑问词+will+主语+谓语动词原型
- 用法:
- 表示将来要发生的事情: I will go to Beijing somedays later.
现在进行时
- 形式
- 肯定形式:主语+be+动词ing
- 否定形式:主语+be+not+doing
- 疑问形式:疑问词+be+主语+doing
- 用法:
- 表示动作正在发生: I am writing my Bolg.
现在完成时
- 形式
- 肯定形式:主语+have/has+done
- 否定形式:主语+have/has+done
- 疑问形式:疑问词+have/has+done
- 用法:
- 表示过去的过去: I have finished my my first year in college.
语态
动词的语态分为主动语态和被动语态。我们主要介绍被动语态。其中有四个问题:
被动语态的定义
动作的承受者作为句子的主语叫做被动语态。
主动与被动语态之间的转换
- 将宾语改成主语。
- 将动词改成be done
- 将主语用by的形式标出,或者省略。
例子:
He gave the book to me.
The book was given to me by him.
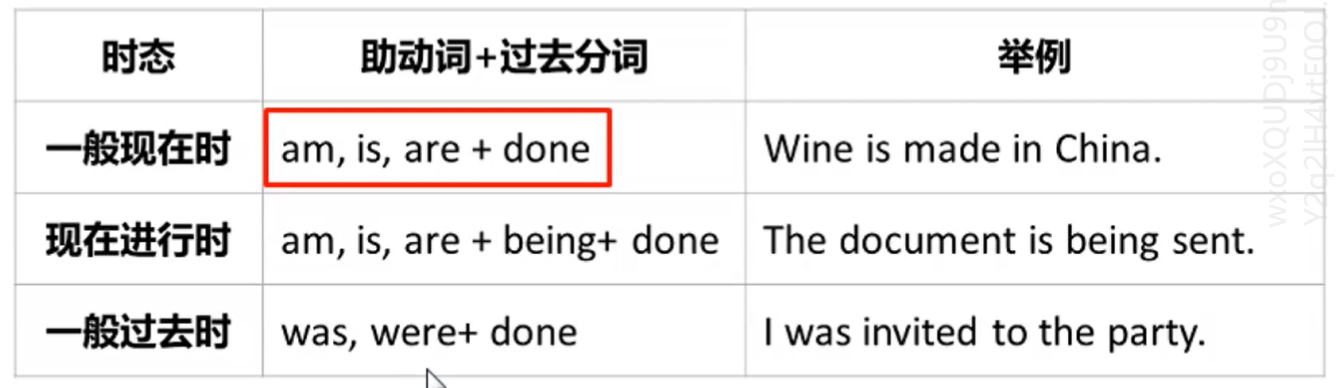

接下来我们介绍几种特殊情况:
- 双宾:
- 把间接宾语改为被动语态的主语,直接宾语保留;
- 把直接宾语改为被动语态的主语,间接宾语要使用to连接。
例:
His teacher gave him a dictionary.
He was given a dictionary by his teacher.
A dictionary was given to him by his teacher.
- 宾补:
如果只有一个词能够作为被动语态的主语则为宾补的情况。
I paint the house white.
The house is painted whited by me. - 加to
不带to的不定时需要增加to.
I let him finished homework.
he was let to finished homework. - 动词短语做谓语
动词短语需要完整保留。
非谓语动词
非谓语动词时英语种一系列不做位于且也不是系动词的用法总称。
非谓语动词的形式
非谓语动词分为三种:不定式 to do,分词 doing/done, 动名词 doing.其中不定时可以做除谓语外的任意成分,而分词只能做定语,状语,补语。动名词相当于名词,其可以做主语,宾语,标表语,定语。
非谓语动词的使用
主语
动词不定式做主语
动词不定式表示不确定,也意味着不一定发生或之后可能发生。
- To save time is to lengthen life.
- It is important to study English well.
动名词做主语
指定是动作发生的过程或者已经确定或者发生的过程。 - Swimming is good exercise.
- It is no use talking to him.
宾语
动词不定式做宾语
动词不定式做宾语也表示不确定,不一定会发生,或者之后可能发生。
- He wants to go to the zoo tomorrow.
- I think it necessary to report the thing to the teacher.
动名词做宾语
指定是动作发生的过程或者已经确定或者发生的过程。 - I enjoy listening to music.
- He is thinking of going abord.
表语
动词不定式做宾语
动词不定式做表语也表示不确定,不一定会发生,或者之后可能发生。
- My ambition is to be a famous singer.
- She seems to go with us.
动名词做表语
指定是动作发生的过程或者已经确定或者发生的过程。 - Jack’s hobby is eating.
定语
不定式、分词、动名词都能够做定语,其用于修饰主语、宾语、表语。
及物动词
- Who is the man standing there?
- This is the sleeping man.
- This is the book written by Luxun in 1918.
- This is the broken window.

不及物动词
不及物动词做非谓语时,to do表示未发生或者不确定,doing 表示正在进行,done表示完成。
状语

非谓语动词的独立主格
接下来我们先比较两句话:
- Singing and dancing, Bobo came in.
Xiao hua singing and dancing, Bobo came in.
独立主格就是在非谓语动词做状语的基础上,非谓语动词不再由主句主语发出。而由独立主格结构的主语发出。名词/代词+doing:表示主动;动作发生或者状态存在
Xiao hua singing and dancing, Bobo came in.
The trees there are extremely tall, some mearsuring over 90 memters.名词/代词+done:表示被动;动作发生或者状态存在
The test finished, we began our holiday.
More time given, I can finish the work.名词/代词+to do:表示主动;动作未发生或者状态未存在
His friends to come tonight, he is busy preparing dinner.
Lots of work to be finished, we have to get up early.
虚拟语气
英语中出现的语气主要由三种,分别是陈述语气、祈使语气和虚拟语气。
- He is honest. (陈述语气)
- Don’t be late next time. (祈使语气)
- If I were you, I would not go. (虚拟语气)
- I wish I had a lot of money. (虚拟语气)
虚拟语气是对暂时不可能实现的事物进行评论时候使用的句式。虚拟语气往往出现在条件句中,虚拟语气就出现在非真实的条件句中。

规律总结:从句都要往过去推一个时态。与现在相反就要使用过去时,与过去相反就要使用过去完成时。
三大从句
英语中的三大从句分别是:定语从句、状语从句、名词性从句。在英语中有三种单词能够被句子替代,分别是:形容词被定语从句替代、副词被状语从句替代、名词被名词性从句替代。
定语从句
- 定语从句:修饰句中的名词或者代词的从句。
- 先行词:指被定语从句修饰的名词或者代词。
- 关系代词/关系副词:引导定语从句的词。
例子:
I know the girl. A girl is talking to Tom.
I know the girl who is talking to Tom.
关系代词
接下来我们介绍不同的关系代词:
当修饰人时:
- 做主语:who,whom,that
- 做宾语:whom,that
- 做定语:whose
修饰物时: - 做主语、宾语:which,that
- 做定语:whose
当定语从句中的介词提前的时候,我们只能使用who/whom/which而不能使用that.
关系副词
关系副词有三个包括:why,when,where.修饰时间用when,地点用where,原因使用why.
名词性从句
名词能够做主语、表语、宾语、同位语。由此产生了主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句。
在名词性从句中连接词的选用仅仅与需要表达的意思有关,而其他成分没有必然联系。
主语从句
在从句中充当主语,例如:
- How the boy behaved was not very polite.
- When he will be there is unsure.
- What she wrote surprised her family.
宾语从句
在主句中充当宾语,例如: - She didn’t realize that the directions were wrong.
- He didn’t know why the stove wasn’t working.
- They now understand that you should not cheat on a test.
同位语从句
在从句中充当宾语,例如: - Our knowledge that students can become independent learners drives our work.
- The issue whether it is right or wrong depends on the result.
- The fact that we will come back soon excited everyone.
表语从句
在从句中充表语,例如: - The foucus of our work is how we can satisfy customers most effectively.
- My greatest asset is that I am a hard-working worker.
状语从句
状语从句用来修饰整个句子,比较灵活,连词的选用主要依据连词的意思。
时间状语从句
- When the outside got dark, Susan’s face turned into dark.
- She gave everyone a present before she left.
- No one left the room until the talk ended.
地点状语从句
- I like to have him next to me where I can keep an eye on him.
注意区分地点状语从句与定语从句,如果修饰前面的名词则为定语从句,否则则为地点状语从句。
原因状语从句
英语中有许多个连词都可以表达因为的意思,because,as,in that…
- Just because I don’t complain. people think I’m satisfied.
- As it was getting to late, I decided to book into a hotel.
- The research is important in that it confirms the link between aggression and alcohol.
让步状语从句
表达尽管的意思的状语从句。
- Despite repeated assurances that the product is safe, many people stopped buying it.
- Although/Though he is very old, he is quite healthy.
- No matter what happened, he would persist.
目的状语从句
表达为了…意义的状语从句,常见连词有In order,for, so that…
- In order that he should not be late again, his mother woke him up at 6:00 am.
- He walked fast for fear that he should be late.
- He works hard at his lessons so that he could perform in the exams.
结果状语从句
表达为了如此…以至于…,常见的引导词有:so…that, such…that,…
- The camera is so expensive that I can’t afford it.
- It was really cold, so that the river froze.
- His plan was such a good one that we all agreed to accept it.
条件状语从句
表达为了如果,常见的引导词有:If, as long as, unless, provided that等等
- If we hurry, we may catch the bus.
- As long as you do that, then the rest is kind of simple and easy.
- Nothing will come of it, unless disaster.
- He’s welcome to come along, provided that he behaves himself.
方式状语从句
表达为了好像的意思,常见的引导词有:as if等
- Eliza remembers everything exactly as if it happened yesterday.
比较状语从句
表达为了好像的意思,常见的引导词有:more…more
